World History
Unit 1 | Stone Age
From Paleolithic chipped stone tools to Neolithic farming villages, the artifacts early humans left behind reveal glimpses of human survival and creativity. Look inside to explore the Keystone Story Arcs, Key Knowledge, and lesson scope and sequence for Unit 1.
Arc 2 Lessons | When the World Changed
What can a Neolithic village reveal about a world transformed by farming?
Lesson 10
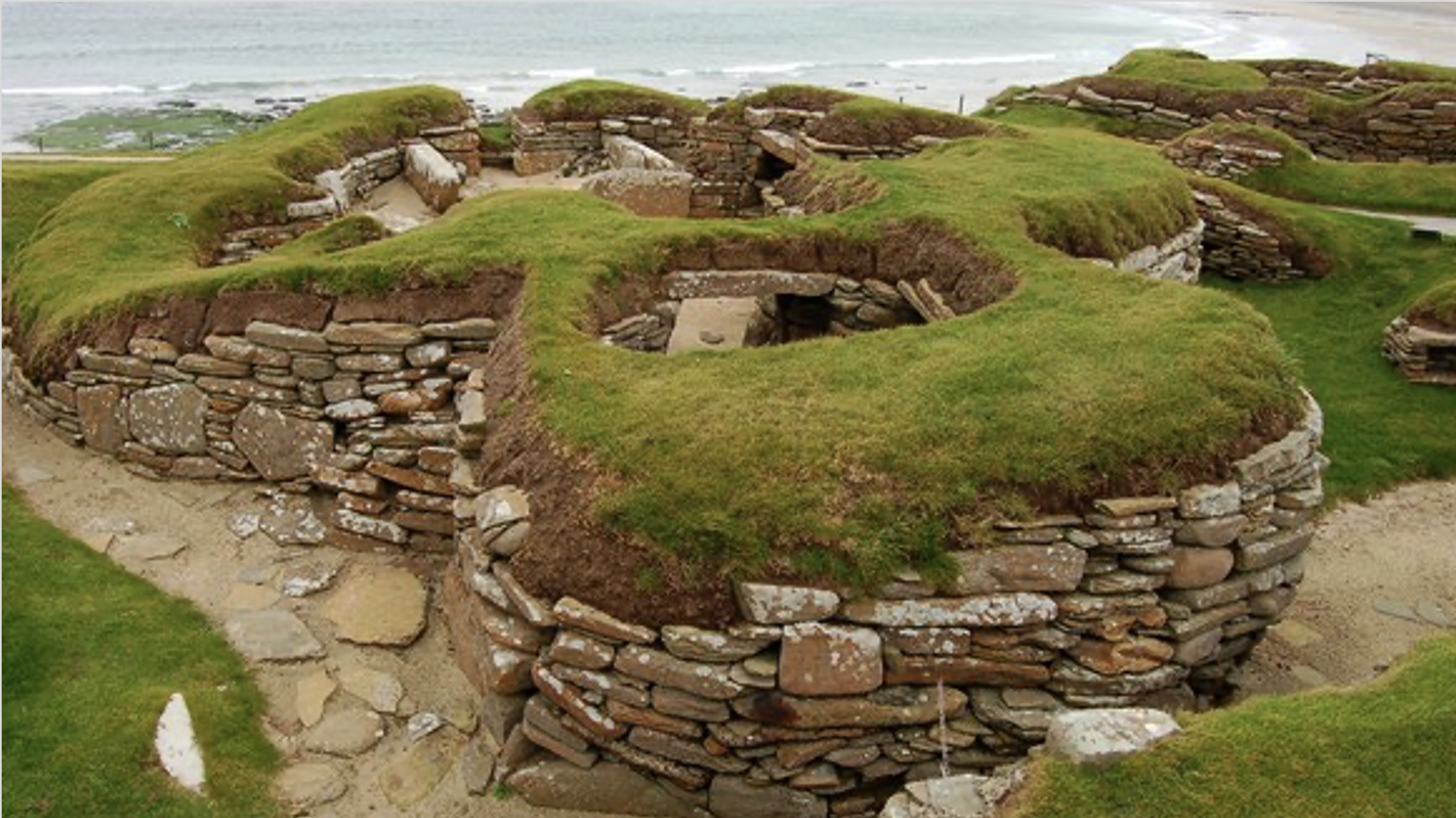
Life Inside These Stone Walls
CLOSELY OBSERVE; ANALYZE USER
Step inside Skara Brae to uncover what Neolithic homes reveal about the people who built them.
Lesson 11
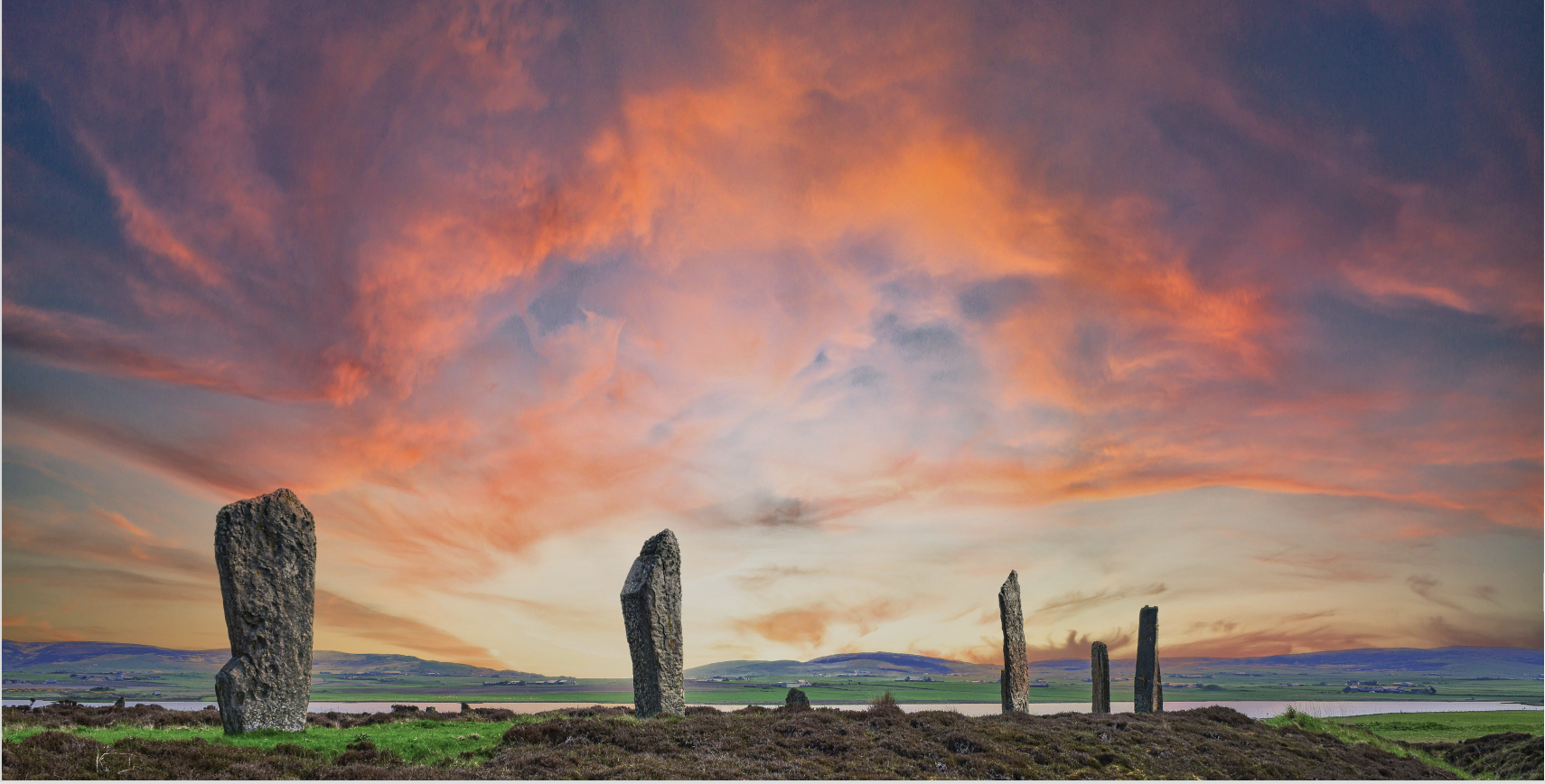
Beyond the Village
PLACE IN CONTEXT
Zoom out to explore sacred spaces that show how Neolithic Orkney people lived, connected, and remembered.
Lesson 12
Mapping a Turning Point
PLACE IN CONTEXT
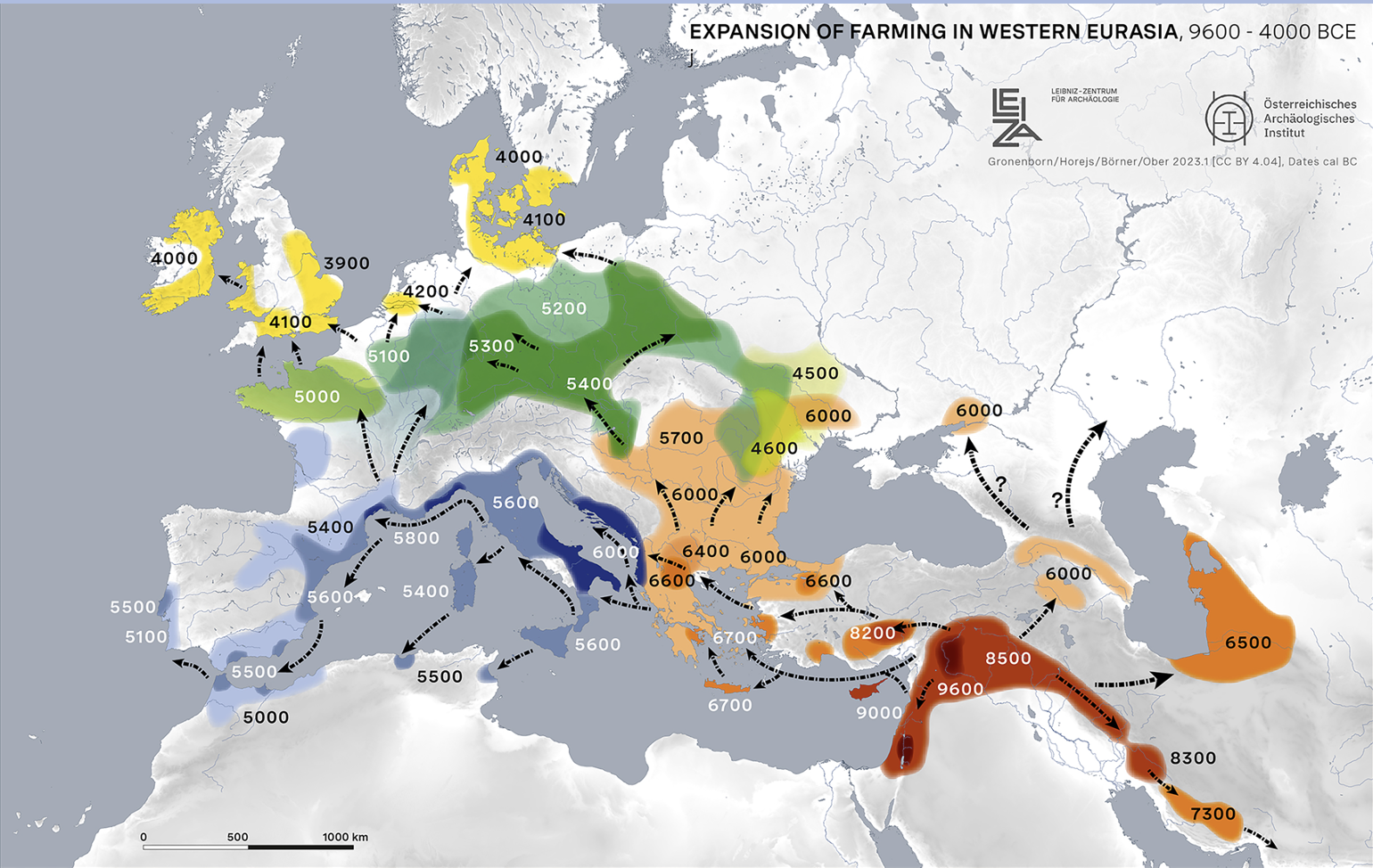
Travel to the Fertile Crescent to discover how geography influenced the spread of farming and reshaped human life.
Lesson 13
Spreading the Seeds of Change
EVALUATE AGAINST OTHER SOURCES
Investigate three theories about how farming spread, then decide which one makes the most sense based on evidence.
Lesson 14
Facts and Conjectures
EVALUATE AGAINST OTHER SOURCES
Every artifact tells a story, but not all stories are certain. Spot conjectures, analyze language, and think critically about what we know and what we’re still wondering.
Lesson 15 (Question Design Lab)
Why Does Farming Matter?
SUMMARIZE SIGNIFICANCE
Synthesize thinking about the impact of the Neolithic Revolution and develop questions about it for the upcoming Socratic Seminar.
Lesson 16 (Assessment)
When the World Changed
SUMMARIZE SIGNIFICANCE
Step into the discussion circle with your evidence as we wrestle with the big question: What changed during the Neolithic Revolution and what made that change a “revolution” for humans?
Free Pilot!
Interested in trying Tapestry in your school or classroom? It will be available for free piloting beginning in March 2026.